Understanding: What Is The Normal A1C Level? +Tips
Is your blood sugar truly under control, or are you unknowingly inching towards serious health complications? The A1C level is the key indicator, offering a vital glimpse into your average blood sugar levels over the past few months, and understanding its normal range is crucial for diabetes management and overall well-being.
The A1C level, also known as hemoglobin A1c, glycated hemoglobin, or HbA1c, is a blood test that reveals your average blood sugar (glucose) levels over the preceding two to three months. Unlike a fasting blood glucose test, which provides a snapshot of your blood sugar at a single moment, the A1C offers a broader perspective, making it a powerful tool for diagnosing prediabetes and diabetes, as well as for monitoring how well people with diabetes are managing their condition. A1C does this by measuring the percentage of your red blood cells that have glucose attached to them. The higher your blood sugar levels, the more glucose will be attached to your red blood cells.
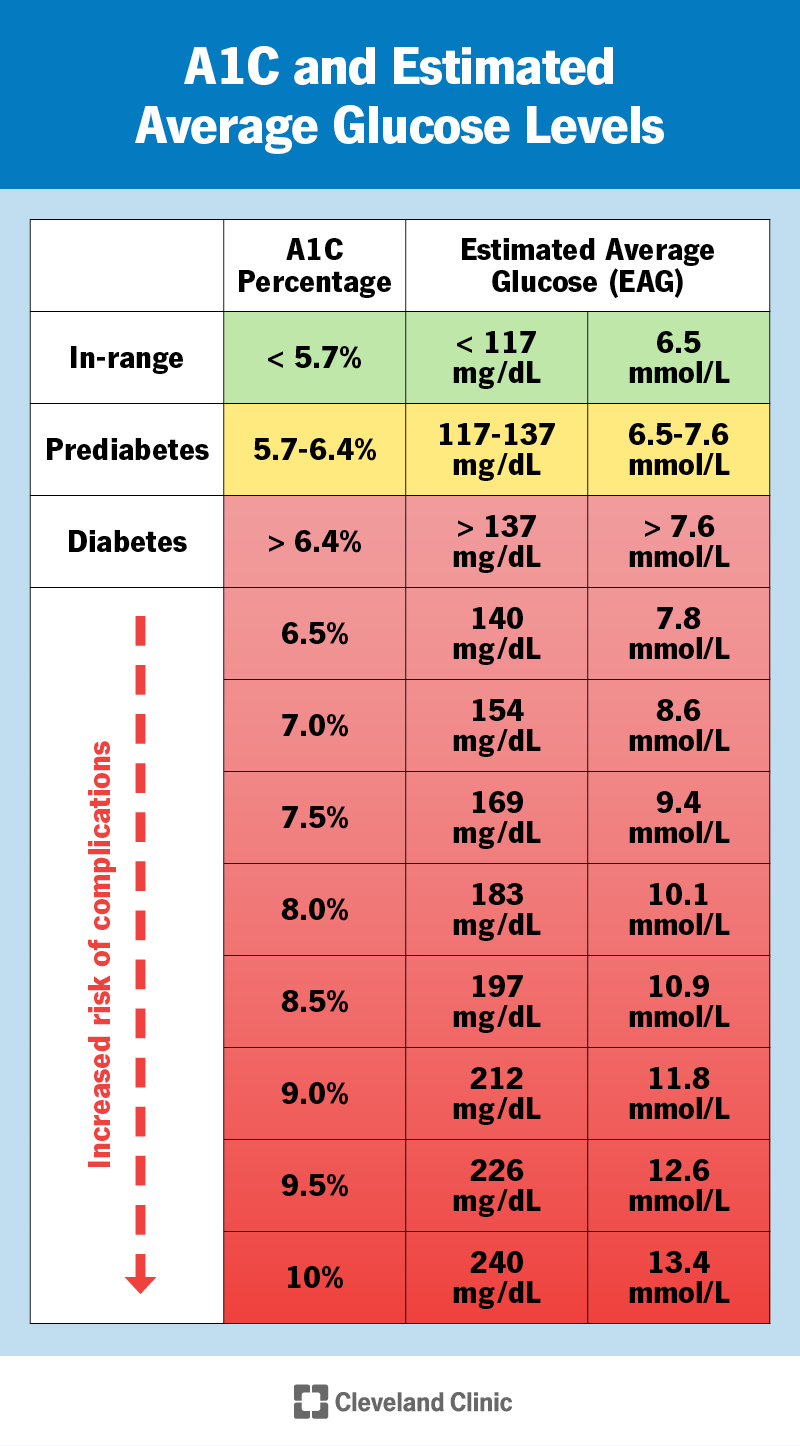
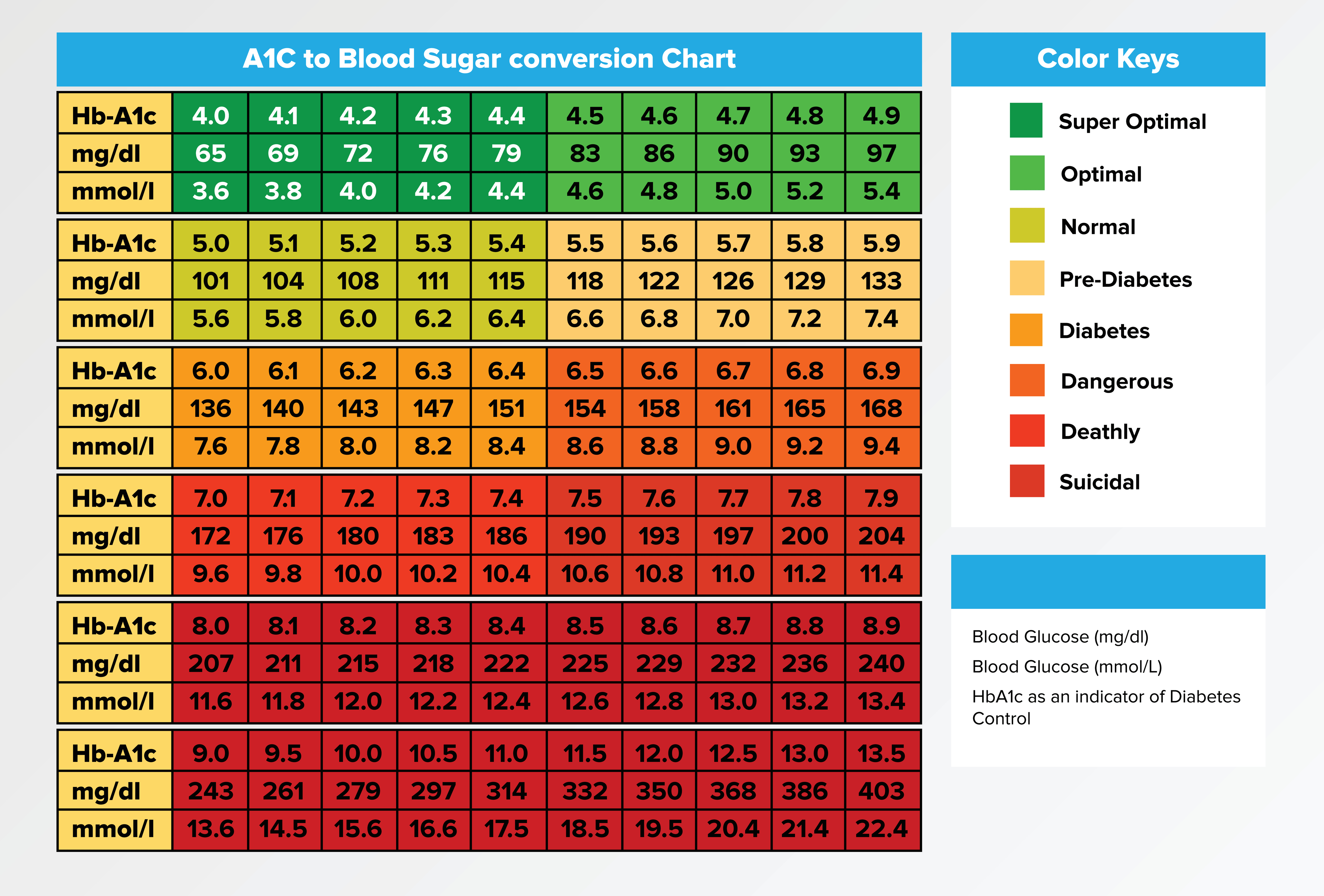
What, then, constitutes a "normal" A1C level? For individuals without diabetes, the generally accepted normal A1C range falls between 4% and 5.6%. An A1C level within this range indicates that your blood sugar levels have been relatively stable and within a healthy range over the past few months. However, if your A1C level consistently exceeds 5.6%, it signals cause for concern.
- Vegamovies Ist Is It Safe Legal The Ultimate Guide
- Ultimate Guide Watch Vegamovies Kdrama Online Free
Specifically, an A1C level between 5.7% and 6.4% indicates prediabetes, a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be classified as diabetes. Prediabetes is a critical warning sign, as it significantly increases your risk of developing type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. An A1C level of 6.5% or higher confirms a diagnosis of diabetes, indicating that your blood sugar levels are chronically elevated.
It's important to note that the target A1C level for individuals with diabetes may be slightly higher than the normal range for those without the condition. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) generally recommends that most adults with diabetes aim for an A1C level below 7%. However, the ideal A1C target may vary depending on individual factors such as age, overall health, and the presence of other medical conditions. Your doctor will work with you to determine the most appropriate A1C target for your specific needs.
Achieving and maintaining a healthy A1C level is crucial for preventing or delaying the onset of diabetes complications. Elevated blood sugar levels, reflected in a high A1C, can damage blood vessels and nerves throughout the body, leading to a cascade of serious health problems. These complications can include heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage (neuropathy), eye damage (retinopathy), and foot problems.
- Who Is Lexi Thompsons Husband All About Cody Matthew Now
- Jyoti Amge Husband The Truth About Her Relationship Status 2023
The good news is that there are numerous steps you can take to lower your A1C level and improve your blood sugar control. These strategies encompass lifestyle modifications, such as adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and, if necessary, taking medications as prescribed by your doctor.
Diet plays a pivotal role in managing blood sugar levels. A diabetes-friendly diet emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein sources, and healthy fats. Limiting your intake of sugary drinks, refined carbohydrates, and saturated and trans fats is also essential.
Regular physical activity is another cornerstone of diabetes management. Exercise helps to improve your body's sensitivity to insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Activities such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming, and cycling can all be beneficial.
In some cases, lifestyle modifications alone may not be sufficient to achieve the desired A1C level. Your doctor may then prescribe medications to help lower your blood sugar. There are various types of diabetes medications available, each working in a different way to improve blood sugar control. Your doctor will determine the most appropriate medication or combination of medications based on your individual needs and medical history.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Full Name | Emily Carter, MD |
| Date of Birth | March 15, 1978 |
| Place of Birth | Chicago, Illinois, USA |
| Education |
|
| Board Certification | Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism |
| Current Position | Director, Diabetes Center, City General Hospital; Professor of Medicine, University School of Medicine |
| Professional Affiliations |
|
| Awards and Honors |
|
| Publications | Over 50 peer-reviewed articles in journals such as "Diabetes Care," "The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism," and "The New England Journal of Medicine." |
| Research Interests | Type 2 Diabetes Prevention, Novel Insulin Therapies, Glucose Monitoring Technologies |
| Contact Information |
|
| Website Reference | American Diabetes Association |
Beyond these core strategies, there are other factors that can influence your A1C level. Certain medical conditions, such as anemia and kidney disease, can affect A1C results, so it's important to inform your doctor about any underlying health issues. Certain medications, such as some HIV drugs, can also interfere with A1C testing.
Regular A1C testing is essential for monitoring blood sugar control and making timely adjustments to your treatment plan. The frequency of A1C testing will depend on your individual circumstances. If you have diabetes, your doctor will typically recommend A1C testing every three to six months. If your blood sugar is well-controlled, you may only need to be tested once a year.
The A1C test is not without its limitations. It provides an average blood sugar level over a period of months, which may mask fluctuations in blood sugar that occur throughout the day. It may also be less accurate in certain populations, such as people with certain types of anemia or hemoglobinopathies. However, despite these limitations, the A1C test remains a valuable tool for assessing long-term blood sugar control.
In addition to the A1C test, people with diabetes often monitor their blood sugar levels at home using a blood glucose meter. This allows them to track their blood sugar levels throughout the day and make adjustments to their diet, exercise, or medication as needed. Home blood glucose monitoring can provide valuable information that complements the A1C test.
The A1C level is also used in research studies to assess the effectiveness of new diabetes treatments and prevention strategies. By tracking A1C levels in large groups of people, researchers can determine whether a particular intervention is effective at improving blood sugar control and reducing the risk of diabetes complications.
The A1C test has revolutionized the way diabetes is managed. Before the A1C test was introduced, doctors had to rely on single blood sugar readings, which could be affected by a variety of factors, such as stress and recent meals. The A1C test provides a more comprehensive and reliable measure of long-term blood sugar control.
Maintaining a healthy A1C level is an ongoing process that requires commitment and collaboration with your healthcare team. By working closely with your doctor, you can develop a personalized plan to manage your blood sugar and reduce your risk of diabetes complications. This plan may include lifestyle modifications, medications, and regular A1C testing.
It's also important to be aware of the symptoms of high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) and low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Hyperglycemia can cause symptoms such as increased thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision, and fatigue. Hypoglycemia can cause symptoms such as shakiness, sweating, dizziness, and confusion. If you experience any of these symptoms, it's important to check your blood sugar and take appropriate action.
The A1C level is just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to managing diabetes. It's important to also focus on other aspects of your health, such as blood pressure, cholesterol, and weight. By taking a holistic approach to your health, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing diabetes complications.
Living with diabetes can be challenging, but it's important to remember that you're not alone. There are many resources available to help you manage your condition, including diabetes education programs, support groups, and online communities. By connecting with others who have diabetes, you can share experiences, learn coping strategies, and find encouragement.
The A1C level is a valuable tool for both diagnosing and managing diabetes. By understanding what the A1C level is, what the normal range is, and how to lower your A1C level, you can take control of your health and reduce your risk of diabetes complications. Remember to talk to your doctor about your A1C level and develop a personalized plan to manage your blood sugar.
The normal A1C level is a measure of your average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. It's an important test for people with diabetes because it can help them manage their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of complications.
The normal A1C level is between 4% and 5.6%. If your A1C level is higher than 5.6%, you have diabetes. If your A1C level is between 5.7% and 6.4%, you have prediabetes.
The normal A1C level is important because it can help you manage your diabetes and reduce your risk of complications. High blood sugar levels can damage your blood vessels and nerves, and lead to serious health problems, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
There are many things you can do to lower your A1C level, including:
- Eating a healthy diet
- Getting regular exercise
- Taking medication if needed
If you have diabetes, it's important to talk to your doctor about how to lower your A1C level and manage your blood sugar levels.
The normal A1C level is a measure of your average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. It's an important test for people with diabetes because it can help them manage their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of complications.
- Definition: The A1C level is a measure of your average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months.
- Normal range: The normal A1C level is between 4% and 5.6%.
- Importance: The A1C level is an important test for people with diabetes because it can help them manage their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of complications.
- How to lower your A1C level: There are many things you can do to lower your A1C level, including eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking medication if needed.
- Risks of high A1C levels: High A1C levels can increase your risk of developing serious health problems, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
The A1C level is an important test for people with diabetes. It can help them manage their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of complications. If you have diabetes, it's important to talk to your doctor about how to lower your A1C level and manage your blood sugar levels.
The A1C level is an important test for people with diabetes because it can help them manage their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of complications. The A1C level is a measure of your average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. This means that it can provide a more accurate picture of your blood sugar control than a single blood sugar reading.
- Role of the A1C level in diabetes management: The A1C level is used to diagnose diabetes and to monitor blood sugar control in people with diabetes. It can help people with diabetes to make lifestyle changes and adjust their medications to improve their blood sugar control.
- Benefits of maintaining a healthy A1C level: Maintaining a healthy A1C level can help to reduce the risk of developing serious health problems, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
- Factors that can affect the A1C level: The A1C level can be affected by a number of factors, including diet, exercise, and medication. It is important to talk to your doctor about how to manage these factors to maintain a healthy A1C level.
- Limitations of the A1C level: The A1C level is not a perfect measure of blood sugar control. It can be affected by factors other than blood sugar levels, such as anemia and certain medications. It is important to talk to your doctor about the A1C level and other factors that may affect your blood sugar control.
The A1C level is an important test for people with diabetes. It can help them manage their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of complications. It is important to talk to your doctor about your A1C level and how to manage your blood sugar control.
The normal A1C level is a measure of your average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. It is an important test for people with diabetes because it can help them manage their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of complications.
- Target range for A1C levels: The target range for A1C levels for most people with diabetes is between 4% and 5.6%. This range is based on studies that have shown that people with A1C levels in this range have a lower risk of developing complications from diabetes, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness.
- Factors that can affect A1C levels: A number of factors can affect A1C levels, including diet, exercise, and medication. It is important to talk to your doctor about how to manage these factors to maintain a healthy A1C level.
- Importance of regular A1C testing: Regular A1C testing is important for people with diabetes to ensure that their blood sugar levels are under control. A1C testing can help to identify problems with blood sugar control early on, so that steps can be taken to adjust treatment and prevent complications.
- Lifestyle changes to improve A1C levels: There are a number of lifestyle changes that can help to improve A1C levels, including eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking medication as prescribed by your doctor.
Maintaining a healthy A1C level is an important part of managing diabetes and reducing your risk of complications. Talk to your doctor about your A1C level and how to make lifestyle changes to improve your blood sugar control.
The A1C level is an important test for people with diabetes because it can help them manage their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of complications. The A1C level is a measure of your average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. This means that it can provide a more accurate picture of your blood sugar control than a single blood sugar reading.
For people with diabetes, it is important to maintain a healthy A1C level. A healthy A1C level can help to reduce the risk of developing serious health problems, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness. The target A1C level for most people with diabetes is between 4% and 5.6%.
There are a number of things that people with diabetes can do to manage their blood sugar levels and maintain a healthy A1C level. These include eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking medication as prescribed by their doctor. Regular A1C testing is also important to ensure that blood sugar levels are under control and to identify problems early on.
Maintaining a healthy A1C level is an important part of managing diabetes and reducing the risk of complications. Talk to your doctor about your A1C level and how to make lifestyle changes to improve your blood sugar control.
Maintaining a healthy A1C level is an important part of managing diabetes and reducing your risk of complications. The A1C level is a measure of your average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. A healthy A1C level is between 4% and 5.6%.
There are a number of things you can do to lower your A1C level, including:
- Eating a healthy diet: A healthy diet for people with diabetes includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It also includes lean protein and low-fat dairy products. Limiting your intake of sugary drinks, processed foods, and unhealthy fats can also help to lower your A1C level.
- Getting regular exercise: Exercise can help to lower your blood sugar levels and improve your insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Taking medication: If diet and exercise are not enough to lower your A1C level, your doctor may prescribe medication. There are a number of different types of diabetes medications available, and your doctor will work with you to find the best one for you.
Working with your doctor to develop a personalized plan to lower your A1C level is important. By following your doctor's recommendations, you can improve your blood sugar control and reduce your risk of developing complications from diabetes.
High A1C levels are a major risk factor for developing serious health problems, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness. This is because high A1C levels can damage the blood vessels and nerves throughout the body.
For example, high A1C levels can damage the blood vessels in the heart, leading to heart disease. High A1C levels can also damage the blood vessels in the brain, leading to stroke. Additionally, high A1C levels can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to kidney disease.
Maintaining a healthy A1C level is essential for reducing your risk of developing these serious health problems. The normal A1C level is between 4% and 5.6%. If your A1C level is higher than 5.6%, you have diabetes. If your A1C level is between 5.7% and 6.4%, you have prediabetes.
If you have diabetes or prediabetes, it is important to work with your doctor to develop a plan to lower your A1C level. This may include eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and taking medication. Lowering your A1C level can help to reduce your risk of developing serious health problems.
This section addresses frequently asked questions regarding the normal A1C level, providing clear and informative answers to enhance understanding.
Question 1: What is the significance of the A1C level for individuals with diabetes?
Answer: The A1C level holds great significance for diabetic individuals as it reflects their average blood sugar levels over the preceding 2-3 months. Regular monitoring of A1C levels enables them to assess the effectiveness of their diabetes management plan and make necessary adjustments to maintain optimal blood sugar control.
Question 2: What are the potential consequences of elevated A1C levels?
Answer: Sustained high A1C levels can lead to severe health complications. Over time, uncontrolled blood sugar levels may damage blood vessels and nerves, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and vision impairment. Therefore, it is crucial for diabetic individuals to maintain their A1C levels within the recommended range.
Summary: Understanding the normal A1C level and its implications for diabetic individuals is essential for effective diabetes management. Regular monitoring and appropriate lifestyle modifications can help maintain healthy A1C levels, reducing the risk of long-term complications and promoting overall well-being.
In summary, the normal A1C level, a measure of average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months, plays a crucial role in diabetes management. Maintaining a healthy A1C level is essential to reduce the risk of developing severe health complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and blindness. Through lifestyle modifications such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and proper medication adherence, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their A1C levels and improve their overall health outcomes.
Regular A1C testing is paramount for monitoring diabetes management effectiveness and making timely adjustments to treatment plans. By working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals with diabetes can optimize their A1C levels, leading to improved blood sugar control, reduced risk of complications, and enhanced quality of life.
- Guide To Vegamovies Download 300mb Is It The Right Choice
- Vegamovies 4k 1080p Watch Movies Online Is Vegamovies Legal
Top 9 what is a dangerous level of a1c 2023

Hemoglobin A1c Test Cost Just at 29 Order Online & Get Tested
Know What A1c Test Measures, Conversion Calculator, Ranges & Tips