Alaska To Russia Distance: Discover Surprising Facts & More!
Ever wondered just how close Alaska and Russia really are? The answer might surprise you: they are separated by such a narrow strip of water that, on a clear day, you might just be able to see one from the other.
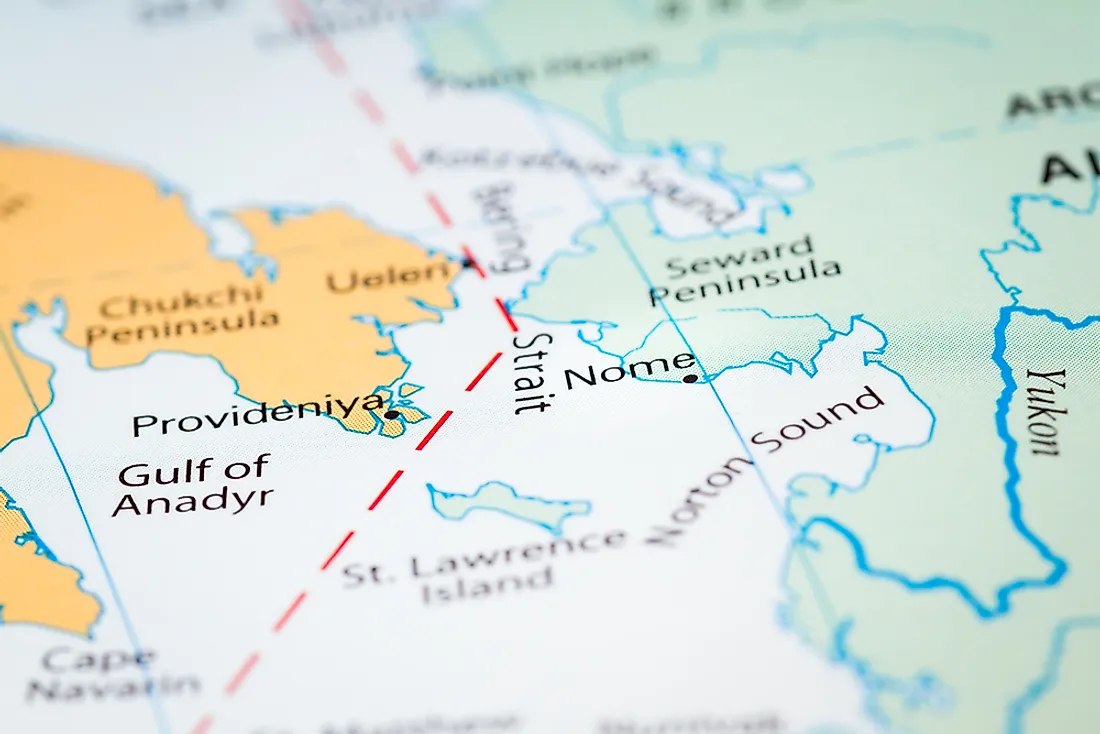
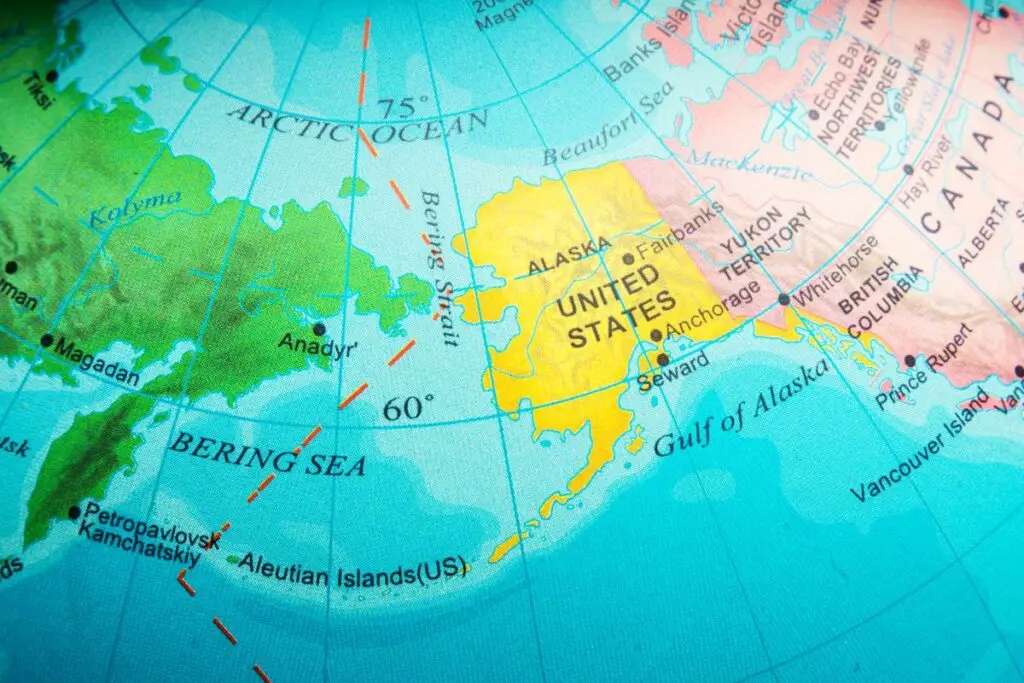
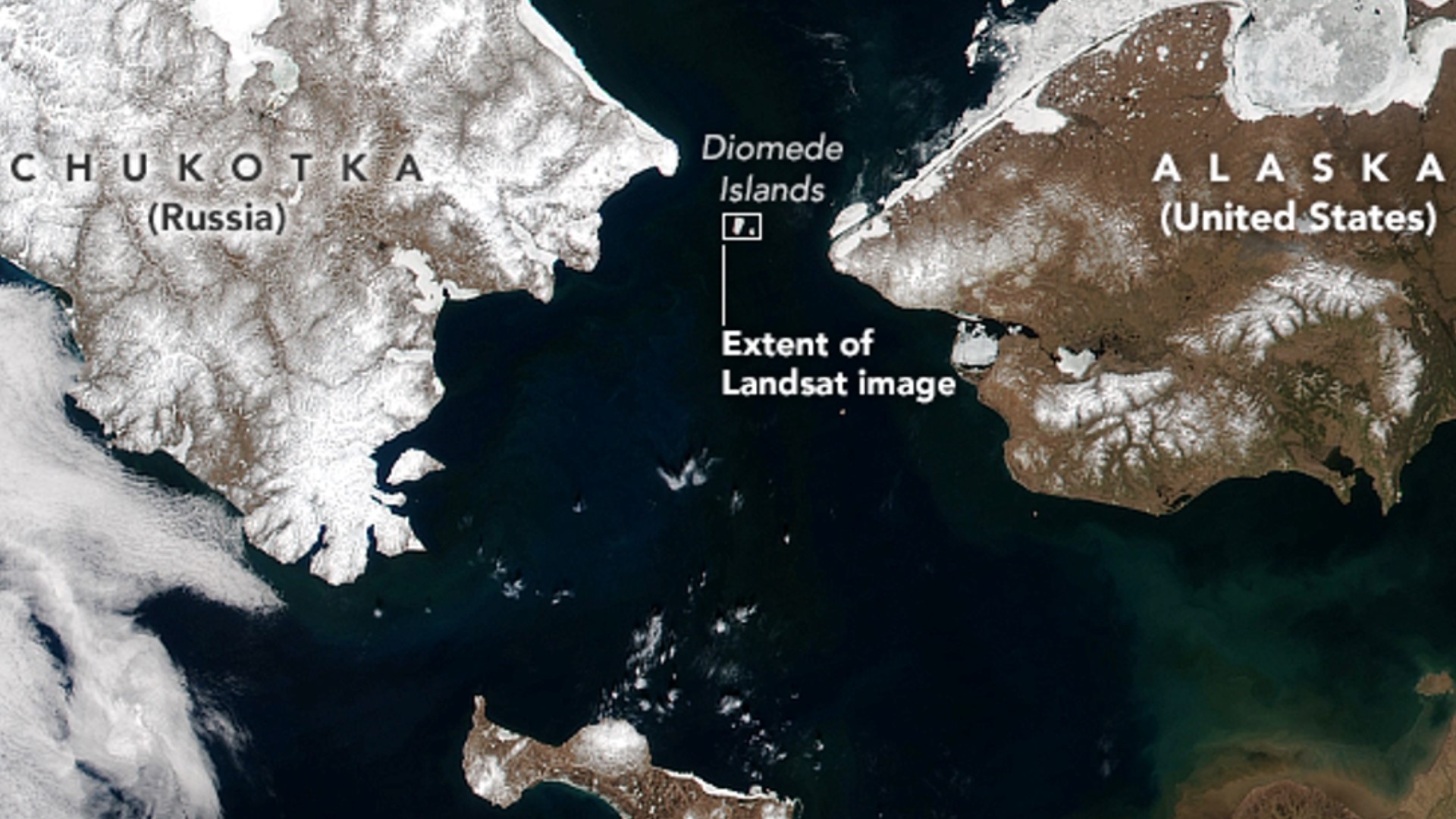
Across the Bering Strait, the distance between Alaska and Russia is a mere 55 miles (89 kilometers). The closest points are Cape Prince of Wales in Alaska and Cape Dezhnev in Russia, two landmasses that stand as silent sentinels observing the ebb and flow of history.
This geographical closeness has profoundly shaped the history and culture of both nations. From early trade routes to a shared heritage, the effects are undeniable. A notable Russian population thrives in Alaska, and the Bering Strait serves as a vital artery for international shipping, significantly contributing to the economic well-being of both countries.
- Everything You Need To Know About Utah Body Rubs Today
- Who Is Connie Kline Young A Look At Her Career Policies
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Closest Points | Cape Prince of Wales, Alaska & Cape Dezhnev, Russia |
| Distance | Approximately 55 miles (89 kilometers) |
| Historical Significance | Trade routes, cultural exchange, and geopolitical considerations. |
| Economic Impact | Major shipping route via the Bering Strait. |
| Cultural Influence | Significant Russian population in Alaska; influence on Alaskan culture. |
The United States Geological Survey (USGS) provides detailed information on the geography of the Bering Strait. For more, visit: USGS Official Website
The proximity of Alaska to Russia, a mere 55 miles across the Bering Strait, has shaped their historical, cultural, and economic connections. Here are seven key aspects that highlight the significance of this distance:
- Geographic proximity: Alaska and Russia are the closest two countries in the world.
- Historical ties: The two countries have a long history of trade and exploration dating back to the 18th century.
- Cultural exchange: There is a significant Russian population in Alaska, and Russian culture has had a major impact on Alaska's development.
- Economic importance: The Bering Strait is a major shipping route, and it is important for both countries' economies.
- Environmental connections: The two countries share similar Arctic ecosystems and face common environmental challenges.
- Strategic significance: The proximity of Alaska to Russia has played a role in military and geopolitical considerations.
- Tourism potential: The close distance between Alaska and Russia offers opportunities for tourism and cultural exchange.
These aspects underscore the multifaceted nature of the relationship between Alaska and Russia. Their proximity has fostered cooperation and exchange while also shaping their respective histories and futures.
- Vegamovies 2024 4k Your Guide To Free 4k Movies Shows
- Guide Is Vegamovies 4k Hd Really Safe Legal Find Out
The geographic proximity of Alaska and Russia has had a profound impact on their relationship. The two countries are separated by just 55 miles across the Bering Strait, making them the closest two countries in the world. This proximity has facilitated centuries of trade, exploration, and cultural exchange. The implications of this singular fact extend far beyond mere cartography, influencing the very fabric of their intertwined destinies.
The Bering Strait, more than just a body of water, has served as a bridge connecting Alaska and Russia, facilitating the movement of people, goods, and ideas. In the 18th century, Russian fur traders, lured by the promise of rich pelts, established settlements in Alaska. This marked the beginning of sustained contact, and even after the United States purchased Alaska from Russia in 1867, many Russians remained, contributing to the state's unique cultural mosaic. Today, a vibrant Russian population continues to thrive in Alaska, and Russian cultural influences are deeply interwoven into the state's identity, manifested in everything from architecture to cuisine.
Furthermore, the geographic proximity of Alaska and Russia has a significant impact on their respective economies. The Bering Strait acts as a crucial maritime highway, a major shipping route that is vital for both nations. Alaska exports a wealth of natural resources, including timber, minerals, and seafood, to Russia, while Russia reciprocates with manufactured goods, machinery, and fuel. This trade relationship is further strengthened by cooperative economic development projects, demonstrating the mutual benefits derived from their close proximity. These projects often focus on sustainable resource management and infrastructure improvements.
However, the closeness also carries security implications. The shared border necessitates ongoing dialogue and cooperation to address common threats, ranging from illegal fishing and smuggling to potential military incursions. While periods of geopolitical tension have punctuated their history, both countries recognize the importance of maintaining stability in the region. Joint exercises and intelligence sharing are common practices aimed at ensuring mutual security. The Arctic, in particular, has become an area of increased focus due to its strategic significance and the impacts of climate change.
Ultimately, the geographic proximity of Alaska and Russia is a cornerstone of their intricate relationship. It has not only shaped their history, culture, and economy but also their approach to security and cooperation. Understanding this dynamic is crucial for navigating the complexities of the 21st century and fostering a future of shared prosperity and stability in the Arctic region.
The proximity of Alaska to Russia has played a significant role in the long history of trade and exploration between the two countries. The Bering Strait has served as a bridge between Alaska and Russia, allowing for the movement of people, goods, and ideas. This narrow waterway has been both a conduit for exchange and a potential chokepoint for conflict, influencing the geopolitical landscape of the region for centuries.
- Russian fur trade: In the 18th century, Russian fur traders, driven by the insatiable demand for luxurious pelts in Europe, established settlements in Alaska. The lucrative fur trade became a major economic activity, attracting adventurers and entrepreneurs alike. These traders meticulously explored vast swaths of Alaska, establishing trading posts along the coast and inland, profoundly altering the indigenous way of life. The competition for resources and control led to both cooperation and conflict with native populations.
- American purchase of Alaska: In 1867, the United States, under the shrewd guidance of Secretary of State William Seward, purchased Alaska from Russia for $7.2 million a deal initially ridiculed as "Seward's Folly." However, the acquisition of Alaska proved to be a stroke of genius, granting the U.S. control of a vast and resource-rich territory in the Arctic. This strategic move not only expanded American influence in the Pacific but also laid the groundwork for future economic and military advantages.
- Cultural exchange: The intertwining of Russian and Alaskan histories, particularly during the fur trade era and the subsequent American purchase, led to a significant exchange of cultural practices. Russian Orthodox missionaries established churches and schools, leaving a lasting impact on the religious landscape of Alaska. Russian architectural styles, culinary traditions, and linguistic influences continue to be evident in many Alaskan communities today. Conversely, indigenous Alaskan cultures influenced Russian customs and traditions, creating a unique blend of influences.
- Cooperation and conflict: The history of Alaska and Russia is characterized by a complex interplay of cooperation and conflict, mirroring the broader geopolitical dynamics between the two nations. While periods of dtente and collaboration have occurred, particularly in areas such as environmental protection and resource management, tensions have also arisen, particularly during the Cold War. The Arctic became a strategic battleground, with both countries vying for dominance and control of vital resources and strategic locations. The legacy of the Cold War continues to shape the security landscape of the region.
The long history of trade and exploration between Alaska and Russia serves as a compelling testament to the enduring relationship between the two countries. This proximity has facilitated centuries of exchange and cooperation, albeit interspersed with periods of tension and conflict, leaving an indelible mark on their respective identities and shaping the geopolitical dynamics of the Arctic region. The Bering Strait remains a vital link, both geographically and historically, binding these two nations together in a complex and evolving relationship.
The proximity of Alaska to Russia has fostered centuries of cultural exchange between the two regions, creating a fascinating blend of traditions, languages, and beliefs. This cross-cultural pollination has shaped the identity of both Alaska and Russia, leaving an indelible mark on their respective societies.
The initial wave of cultural exchange began with the arrival of Russian fur traders in Alaska during the 18th century. These traders established settlements and trading posts, introducing Russian language, customs, and religion to the indigenous populations. Russian Orthodox missionaries played a particularly influential role, converting many Alaskans to Christianity and establishing churches and schools that served as centers of cultural dissemination.
Following the United States' purchase of Alaska from Russia in 1867, many Russians chose to remain in the territory, contributing to the continued presence of Russian culture in the region. These Russian immigrants maintained their traditions, passed on their language to subsequent generations, and played an active role in shaping Alaskan society.
Even today, the Russian cultural influence is palpable throughout Alaska. Russian Orthodox churches dot the landscape, serving as enduring symbols of the historical connection between the two regions. Russian festivals and traditions are celebrated in many communities, showcasing the vibrant heritage of Russian Alaskans. The Russian language is still spoken by many Alaskans, particularly in rural areas, and Russian place names are ubiquitous throughout the state, serving as a constant reminder of the past.
This cultural exchange has not been a one-way street. Indigenous Alaskan cultures have also influenced Russian society, particularly in the Russian Far East. Russian traders and settlers adopted aspects of indigenous Alaskan culture, learning survival skills, incorporating native art forms into their crafts, and even intermarrying with indigenous women. This reciprocal exchange has enriched both cultures, creating a unique tapestry of traditions.
The cultural exchange between Alaska and Russia stands as a powerful testament to the enduring impact of proximity and interaction. It highlights the transformative power of cultural exchange, demonstrating how different societies can learn from each other, adapt to new environments, and create vibrant and unique cultural identities. The legacy of this exchange continues to shape the relationship between Alaska and Russia, fostering a sense of shared heritage and promoting cross-cultural understanding.
The Bering Strait, the narrow waterway separating Alaska and Russia, holds immense economic importance for both nations and the broader global economy. This strategic waterway serves as a vital maritime artery, facilitating trade, transportation, and resource extraction, thereby contributing significantly to the economic prosperity of both countries.
The Bering Strait serves as a major shipping route connecting the Pacific and Arctic Oceans. This route is utilized by cargo ships transporting goods between Asia, North America, and Europe, making it a critical link in the global supply chain. The proximity of Alaska to Russia makes the Bering Strait particularly important for both countries, allowing them to participate in this global trade network.
The Bering Strait is also a key transportation route for resources extracted from the Arctic region. Oil, gas, and minerals are transported through the Bering Strait to markets around the world, generating significant revenue for both Alaska and Russia. As climate change melts Arctic ice, the Bering Strait is expected to become an even more important transportation route, opening up new opportunities for resource extraction and trade.
In addition to its role in trade and transportation, the Bering Strait is also a rich fishing ground, providing a valuable source of seafood for both Alaska and Russia. The waters of the Bering Strait are teeming with fish, crab, and other marine species, supporting a thriving fishing industry that employs thousands of people and contributes billions of dollars to the economies of both countries.
Recognizing the economic importance of the Bering Strait, both Alaska and Russia have established a joint commission to manage the waterway and ensure its safe and sustainable use. This commission promotes cooperation on issues such as maritime safety, environmental protection, and fisheries management, thereby safeguarding the economic interests of both countries.
The economic importance of the Bering Strait is undeniable. It serves as a vital transportation route, a key source of natural resources, and a rich fishing ground, all of which contribute significantly to the economies of both Alaska and Russia. As climate change transforms the Arctic region, the economic importance of the Bering Strait is expected to grow, further solidifying its role as a critical waterway for global trade and resource management.
The geographical proximity of Alaska and Russia dictates that they share a common environmental landscape and, consequently, a shared responsibility for the health of the Arctic ecosystem. This closeness results in intertwined environmental challenges, necessitating collaborative efforts to address issues like climate change, pollution, and the preservation of biodiversity.
- Climate change: The Arctic region is warming at an alarming rate, far exceeding the global average. This phenomenon, primarily driven by greenhouse gas emissions, is causing widespread melting of sea ice, thawing of permafrost, and changes in ocean currents. These changes have profound implications for both Alaska and Russia, threatening coastal communities, disrupting ecosystems, and releasing greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. The proximity of the two regions means that they experience these impacts in a connected way, requiring coordinated efforts to mitigate and adapt to the effects of climate change.
- Pollution: The Arctic acts as a sink for pollutants transported from around the globe via atmospheric and oceanic currents. These pollutants, including persistent organic pollutants (POPs), heavy metals, and plastic debris, accumulate in the Arctic food web, posing risks to wildlife and human health. Both Alaska and Russia face the challenge of managing pollution sources within their territories and working together to address transboundary pollution issues. The shared nature of the Arctic environment necessitates a collaborative approach to monitoring pollution levels, identifying pollution sources, and implementing effective pollution control measures.
- Overfishing: The Arctic Ocean is home to a diverse array of fish species that support both commercial fisheries and the livelihoods of indigenous communities. Overfishing can deplete fish stocks, disrupt the delicate balance of the Arctic ecosystem, and threaten the food security of local populations. Alaska and Russia share several important fish stocks, requiring cooperative management to ensure sustainable fishing practices. This involves setting catch limits, monitoring fishing activities, and enforcing regulations to prevent overfishing and protect vulnerable species.
- Habitat loss: The development of oil and gas resources, mining activities, and infrastructure projects can lead to habitat loss and fragmentation, threatening the survival of Arctic wildlife. Both Alaska and Russia face the challenge of balancing economic development with the need to protect critical habitats. This requires careful planning, environmental impact assessments, and the implementation of mitigation measures to minimize the impacts of development on Arctic ecosystems. Collaboration between the two countries is essential to ensure that development activities are conducted in a sustainable manner that protects the unique biodiversity of the Arctic region.
The environmental challenges facing Alaska and Russia are complex and interconnected, demanding a collaborative approach to protect the fragile Arctic ecosystem. By working together, the two countries can address issues such as climate change, pollution, overfishing, and habitat loss, ensuring the long-term health and sustainability of the Arctic region. The shared environment necessitates a shared responsibility, fostering a spirit of cooperation and mutual understanding.
The geographical proximity of Alaska and Russia inherently imbues the region with considerable strategic significance, influencing military planning, geopolitical strategies, and international relations. The narrow expanse of the Bering Strait creates a unique environment where both countries' actions have direct and immediate implications for the other, shaping their respective security postures and diplomatic approaches.
During the Cold War, Alaska served as a critical strategic outpost for the United States, acting as a bulwark against potential Soviet aggression. The state hosted numerous military bases, radar installations, and early warning systems, designed to detect and deter Soviet aircraft and missiles. Alaska's proximity to Russia made it an ideal location for monitoring Soviet military activities in the Arctic and Pacific regions.
While the end of the Cold War diminished the immediate threat of large-scale military conflict, the Arctic region has once again emerged as a focal point of strategic competition. Climate change has opened up new sea routes and access to valuable natural resources, attracting the attention of various nations, including Russia, the United States, China, and Canada.
Russia has been actively strengthening its military presence in the Arctic, modernizing its Northern Fleet, reopening Soviet-era military bases, and conducting military exercises in the region. These actions have raised concerns among some Western observers, who fear that Russia is seeking to assert its dominance over the Arctic and control access to its resources.
The United States has responded by increasing its military presence in Alaska, conducting joint exercises with allies, and investing in new technologies to enhance its capabilities in the Arctic. The US military recognizes the need to maintain a credible presence in the region to deter potential aggression and protect its interests.
The strategic significance of Alaska and Russia extends beyond military considerations. The region is also important for its economic potential, including its vast reserves of oil, gas, and minerals. Control over these resources could have significant implications for global energy markets and geopolitical power dynamics.
The proximity of Alaska and Russia underscores the importance of maintaining open lines of communication and fostering cooperation to avoid misunderstandings and prevent escalation of tensions. Dialogue, transparency, and adherence to international law are essential to managing the strategic challenges and opportunities presented by this unique region.
The strategic significance of the region is further amplified by the increasing accessibility of the Arctic due to climate change. This creates both opportunities and risks, necessitating careful management and international cooperation.
The close proximity between Alaska and Russia offers remarkable opportunities for tourism and cultural exchange, inviting travelers to explore the unique blend of natural beauty, historical richness, and cultural diversity that characterizes the region. This geographical closeness facilitates cross-border travel and promotes understanding and appreciation between the two cultures.
Alaska and Russia share a long and intertwined history, dating back to the era of Russian exploration and colonization. This shared history is reflected in the numerous cultural similarities between the two regions, including language, religion, art, and traditions. Visitors can explore Russian Orthodox churches in Alaska, attend Russian cultural festivals, and learn about the legacy of Russian influence on Alaskan society.
Both Alaska and Russia boast stunning natural landscapes, ranging from towering mountains and glaciers to vast tundra and boreal forests. These pristine environments offer unparalleled opportunities for outdoor recreation, including hiking, fishing, wildlife viewing, and adventure travel. Visitors can witness the breathtaking beauty of the Northern Lights, explore remote wilderness areas, and encounter iconic Arctic wildlife such as polar bears, whales, and caribou.
The growing interest in adventure travel and cultural tourism has fueled the development of new tourism initiatives and infrastructure in both Alaska and Russia. Several tour operators offer packages that combine visits to both regions, allowing travelers to experience the best of both worlds. These tours often include visits to cultural sites, historical landmarks, and natural attractions, providing a comprehensive overview of the region's unique character.
Tourism has the potential to generate significant economic benefits for both Alaska and Russia, creating jobs, supporting local businesses, and promoting sustainable development. By attracting visitors from around the world, tourism can help to diversify the economies of these regions and contribute to their long-term prosperity.
In addition to economic benefits, tourism can also promote cross-cultural understanding and foster goodwill between Alaska and Russia. By interacting with local communities, learning about different cultures, and sharing experiences, visitors can help to break down stereotypes, build bridges of understanding, and promote peaceful relations between the two countries.
The potential for tourism and cultural exchange between Alaska and Russia is immense. By embracing this opportunity, both regions can reap economic benefits, promote cross-cultural understanding, and create lasting memories for visitors from around the world. The close proximity between the two regions serves as a catalyst for fostering greater cooperation and collaboration in the tourism sector.
This section addresses frequently asked questions about the distance between Alaska and Russia, providing concise and informative answers to common queries.
Question 1: How far apart are Alaska and Russia?
Alaska and Russia are separated by a distance of approximately 55 miles (89 kilometers) at their closest point. This proximity makes them the two closest countries in the world.
Question 2: What is the significance of the distance between Alaska and Russia?
The proximity of Alaska to Russia has had a significant impact on their relationship throughout history. It has facilitated trade, cultural exchange, and cooperation, while also playing a role in military and geopolitical considerations.
Summary: The distance between Alaska and Russia is a key factor in understanding the relationship between the two countries. It has shaped their history, culture, economy, and security.
- Who Is Beau Garretts Partner All About Chris Payne Gilbert
- Vegamovies 4k Is It Safe Legal Plus Free Movie Streaming
How Far is Russia From Alaska? WorldAtlas
How Far Is Russia From Alaska? It's Closer Than You Think!
How far is Russia from the United States