Understanding Painless Ways To Die: Choices & Considerations
In the face of immense suffering, should individuals have the right to choose a peaceful exit? The quest for a painless death, often intertwined with the concept of euthanasia, sparks intense debate, raising profound questions about autonomy, ethics, and the very definition of a dignified end.
Many factors influence the possibility of a painless death. These encompass the root cause of mortality, the individual's overall physical condition, and the accessibility of adequate medical support. In certain instances, a swift cardiac arrest or a substantial cerebral event might induce immediate unconsciousness, culminating in a painless demise. Conversely, in cases involving prolonged ailments like cancer or cardiovascular conditions, the body undergoes a gradual decline, potentially leading to a serene transition.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Concept | Painless Death / Euthanasia |
| Definition | The practice of intentionally ending a life to relieve intractable suffering. |
| Legal Status | Legal in some countries (Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland), illegal in many others. |
| Medical Procedure | Typically performed by a doctor, often using a lethal injection. |
| Ethical Concerns | Moral right to take a life, potential for abuse, "slippery slope" argument. |
| Religious Views | Some religions (e.g., Catholicism) oppose euthanasia on grounds of the sanctity of life. |
| Decision Making | Personal choice, ideally made in consultation with doctors and loved ones. |
| Related Information | End-of-life care, palliative care, patient autonomy. |
| Reference Website | Euthanasia International |
The profound impact of a painless death cannot be overstated. For the individual, it can offer a sense of resolution and tranquility, easing the passage from existence to non-existence. For those left behind family and friends it can mitigate the emotional distress associated with bereavement. Knowing that a loved one departed serenely, free from anguish, provides a measure of comfort and closure.
- Decoded To Whom It No Longer Concerns Chapter 13 More
- Unlock Kosta Kecmanovic Video What To Watch Why It Matters Now
Painless death, frequently synonymous with euthanasia, represents the deliberate termination of life to alleviate unbearable suffering. This remains a fiercely debated subject, with advocates asserting its compassionate nature in ending agony, while opponents deem it morally reprehensible to extinguish a life.
- Legal: Euthanasia is legal in some countries, including the Netherlands, Belgium, and Switzerland.
- Medical: Euthanasia is typically performed by a doctor, using a lethal injection.
- Ethical: Euthanasia raises a number of ethical concerns, including the question of whether it is morally right to take a life.
- Religious: Some religions, such as Catholicism, oppose euthanasia on religious grounds.
- Personal: The decision of whether or not to undergo euthanasia is a personal one, and should be made in consultation with a doctor and loved ones.
The discourse surrounding euthanasia is likely to persist for the foreseeable future. It is essential to acknowledge the complexities inherent in this subject, recognizing that definitive solutions remain elusive. Compelling arguments exist on both sides of the spectrum, necessitating a thorough evaluation of all viewpoints before forming a stance on the endorsement of euthanasia. The core questions revolve around individual rights, societal responsibilities, and the definition of a life worth living.
The formal sanctioning of euthanasia in specific nations wields substantial influence over the availability of methods for a painless departure. In these jurisdictions, individuals grappling with terminal conditions or excruciating discomfort can seek medical intervention to conclude their lives with serenity and dignity.
- Discover Court 8610 The Future Of Basketball Is Here
- Vegamovies Dog Your Guide To Free Movies Tv Shows Year
- Access to Medical Expertise: Within countries where euthanasia is legalized, individuals gain access to healthcare professionals skilled in administering lethal injections. This assures a secure and humane execution, minimizing potential pain or distress. The procedure is carefully orchestrated to ensure the patient's comfort and peace of mind.
- Legal Protection: The legalization of euthanasia provides legal protection for both the individuals seeking to end their lives and the medical professionals assisting them. This protection reduces the risk of prosecution or legal challenges, allowing individuals to make end-of-life decisions without fear of legal repercussions.
- Regulation and Oversight: Nations permitting euthanasia typically institute stringent regulations and monitoring protocols to guarantee adherence to specific criteria and safeguards. This prevents misuse and ensures that individuals are thoroughly informed and competent to make decisions about their own deaths. A multi-layered review process is often in place to validate each request.
- Cultural and Societal Attitudes: The legalization of euthanasia in certain countries reflects a shift in cultural and societal attitudes towards end-of-life care. It recognizes the individual's right to autonomy and self-determination, even in the face of terminal illness or unbearable suffering. The societal acceptance of this option is often a result of extensive public debate and education.
The legalization of euthanasia in certain countries presents a viable option for individuals confronting the end of their lives, seeking a dignified and painless exit. While acknowledging the ongoing controversy surrounding euthanasia and its lack of universal acceptance, its potential to alleviate suffering and provide a peaceful conclusion for those with terminal illnesses or unbearable pain remains significant. The ethical considerations remain at the forefront of the discussion, requiring continuous reflection and refinement of guidelines.
The professional medical execution of euthanasia is an indispensable component of a painless passing, ensuring a secure, humane, and minimally discomforting process. When administered by qualified healthcare providers, lethal injections provide a controlled and effective method of ending life. The selection of medications and the method of administration are carefully considered to ensure the patient's comfort and a swift, peaceful transition.
Lethal injections involve the administration of a combination of drugs, typically including a sedative, a muscle relaxant, and a paralytic agent. The sedative induces unconsciousness, the muscle relaxant prevents involuntary muscle movements, and the paralytic agent stops breathing. This combination of drugs ensures a peaceful and painless death. The specific dosages and combinations are tailored to the individual's medical condition and physical characteristics.
The engagement of medical professionals in euthanasia is vital for several reasons. First, it guarantees that the procedure is executed with utmost diligence and precision. Doctors receive specialized training in administering lethal injections, possessing the expertise to minimize potential discomfort or pain. Second, medical oversight safeguards against misuse, ensuring that euthanasia is performed only according to stringent criteria and safeguards. Physicians are obligated to evaluate the patient's condition, confirm their full awareness and competence in making decisions about their own death, and obtain explicit consent. The process is designed to protect the patient's rights and ensure that their wishes are respected.
Medical euthanasia, when performed in a safe and regulated manner, provides individuals with a dignified and painless way to end their lives. It allows them to maintain control over their own deaths and to avoid prolonged suffering or a loss of autonomy due to terminal illness or unbearable pain. The emphasis is on patient-centered care, ensuring that the individual's values and preferences are honored throughout the process.
The ethical dimension of euthanasia is a complex and multifaceted one, with proponents and opponents offering a range of arguments based on moral, religious, and philosophical principles. At the heart of the debate lies the fundamental question of whether it is morally right to intentionally end a human life, even in cases of terminal illness or unbearable suffering. The debate highlights the tension between individual autonomy and societal values.
Those who support the legalization of euthanasia often argue that it is a compassionate and humane way to end suffering and that individuals should have the right to make decisions about their own deaths. They contend that in cases where an individual is terminally ill or experiencing unbearable pain, euthanasia can provide a dignified and peaceful way to die, rather than enduring prolonged suffering or a loss of autonomy. The focus is on alleviating suffering and respecting the patient's wishes.
Opponents of euthanasia, on the other hand, argue that it is morally wrong to take a life, regardless of the circumstances. They believe that life is sacred and that it should be protected at all costs. They also raise concerns about the potential for abuse and the slippery slope argument, suggesting that legalizing euthanasia could lead to a devaluation of life and a decrease in the value placed on caring for the sick and dying. The emphasis is on protecting vulnerable populations and upholding the sanctity of life.
The ethical debate over euthanasia is likely to continue for many years to come. However, it is important to recognize that this is a complex issue with no easy answers. There are strong arguments on both sides of the debate, and it is important to consider all of the ethical, moral, and religious implications before forming an opinion on this controversial topic. Open dialogue and careful consideration of all perspectives are essential for navigating this complex ethical landscape.
The opposition of certain religions, such as Catholicism, to euthanasia on religious grounds has a significant impact on the availability and perception of painless ways to die. Religious beliefs and teachings play a crucial role in shaping societal attitudes towards end-of-life care and decision-making. The influence of religious doctrine can significantly impact public policy and individual choices.
For example, the Catholic Church maintains a firm stance against euthanasia, viewing it as a grave violation of the sanctity of life. This position is rooted in the belief that human life is sacred and inviolable from the moment of conception until natural death. According to Catholic doctrine, euthanasia is considered a form of murder and is therefore morally wrong. This unwavering stance influences the beliefs and actions of millions of Catholics worldwide.
The influence of religious beliefs on the availability of painless ways to die can be observed in countries where the Catholic Church holds a strong presence and influence over healthcare policies and practices. In such countries, the legalization and practice of euthanasia may face significant resistance and opposition from religious groups and institutions. The power of religious institutions to shape public opinion and policy cannot be underestimated.
This opposition can lead to limited access to euthanasia as a painless way to die, even for individuals who are terminally ill or experiencing unbearable suffering. It can also create a social stigma around euthanasia, making it difficult for individuals to openly discuss or consider it as an end-of-life option. The social and emotional consequences of this stigma can be profound.
Understanding the religious dimension of euthanasia is essential for gaining a comprehensive perspective on the topic of painless ways to die. By considering the influence of religious beliefs and teachings, we can better appreciate the complexities and challenges surrounding end-of-life care and decision-making. A nuanced understanding of these religious perspectives is crucial for fostering respectful and informed discussions.
The personal nature of euthanasia decisions underscores the importance of individual autonomy and self-determination in end-of-life care. When faced with a terminal illness or unbearable suffering, individuals should have the right to make choices about their own death, in consultation with medical professionals and their loved ones.
- Respect for Autonomy: Euthanasia decisions are deeply personal and should be respected as expressions of an individual's autonomy. Respecting autonomy means recognizing the right of competent adults to make decisions about their own lives, even if those decisions involve ending their lives. This respect for individual choice is a cornerstone of ethical medical practice.
- Informed Consent: Before making a decision about euthanasia, individuals should be fully informed about their medical condition, prognosis, and alternative treatment options. This informed consent process ensures that individuals are making decisions based on a clear understanding of their situation. Transparency and honesty are paramount in this process.
- Emotional and Psychological Support: End-of-life decisions can be emotionally and psychologically challenging for individuals and their loved ones. Consultation with a doctor and loved ones can provide invaluable support during this difficult time, helping individuals to process their emotions and make informed choices. Access to counseling and support groups can be incredibly beneficial.
- Balancing Personal Wishes and External Perspectives: While personal wishes should be central to euthanasia decisions, it is also important to consider the perspectives of loved ones and medical professionals. This balanced approach helps to ensure that decisions are made with thoughtful consideration of all relevant factors. Open communication and empathetic listening are essential for navigating these complex dynamics.
Recognizing the personal nature of euthanasia decisions is crucial for upholding the dignity and autonomy of individuals facing end-of-life choices. By respecting autonomy, ensuring informed consent, providing emotional support, and balancing personal wishes with external perspectives, we can create a supportive environment for individuals to make informed and compassionate decisions about their own deaths. The goal is to empower individuals to make choices that align with their values and beliefs.
This section addresses common concerns and misconceptions surrounding painless ways to die, providing informative answers based on reliable sources and expert opinions. The aim is to provide clarity and dispel misinformation.
Question 1: Is euthanasia legal and accessible in all countries?
No, euthanasia is not legal and accessible in all countries. The legality of euthanasia is varied around the world. Certain countries allow the process under strict regulation while some countries prohibit it completely. Conducting proper research about the legal status of euthanasia in one's region is an important thing to consider before further decision making.
Question 2: Are there any religious or ethical concerns associated with euthanasia?
Yes, the concept of euthanasia results in both religious and ethical issues. Some religions like that of Catholicism consider euthanasia as a breach to sanctity of life. Ethical concerns can include the potential of abuse, the slippery slope argument, and the devaluing of life.
Summary: Painless methods of death are sensitive and complex topics which possess legal, medical, ethical, and personal dimensions. Having the subject be approached in the most empathetic and respectful way is the ideal. The various perspectives and considerations involved allow proper decisions and support to be given to those that face end of life choices.
This article has explored the complex and multifaceted nature of painless ways to die, examining its legal, medical, ethical, and personal dimensions. We have seen that euthanasia, a form of assisted dying, is legal in some countries but remains controversial due to religious and ethical concerns. The legal landscape continues to evolve, reflecting shifting societal attitudes.
As we navigate the complexities of end-of-life care, it is essential to approach this topic with empathy, compassion, and respect for individual autonomy. By understanding the different perspectives and considerations involved, we can make informed decisions and support individuals facing end-of-life choices. The ongoing dialogue and research surrounding painless ways to die will continue to shape our understanding of this sensitive and profoundly human issue. Further research is needed to address the many unanswered questions surrounding this complex topic.
- Discover Vega Movie Nl Your Guide To Dutch Streaming
- Kimberly Martins Husband All About Brad Paisley 2024 Update

What's the best method for a painless suicide?
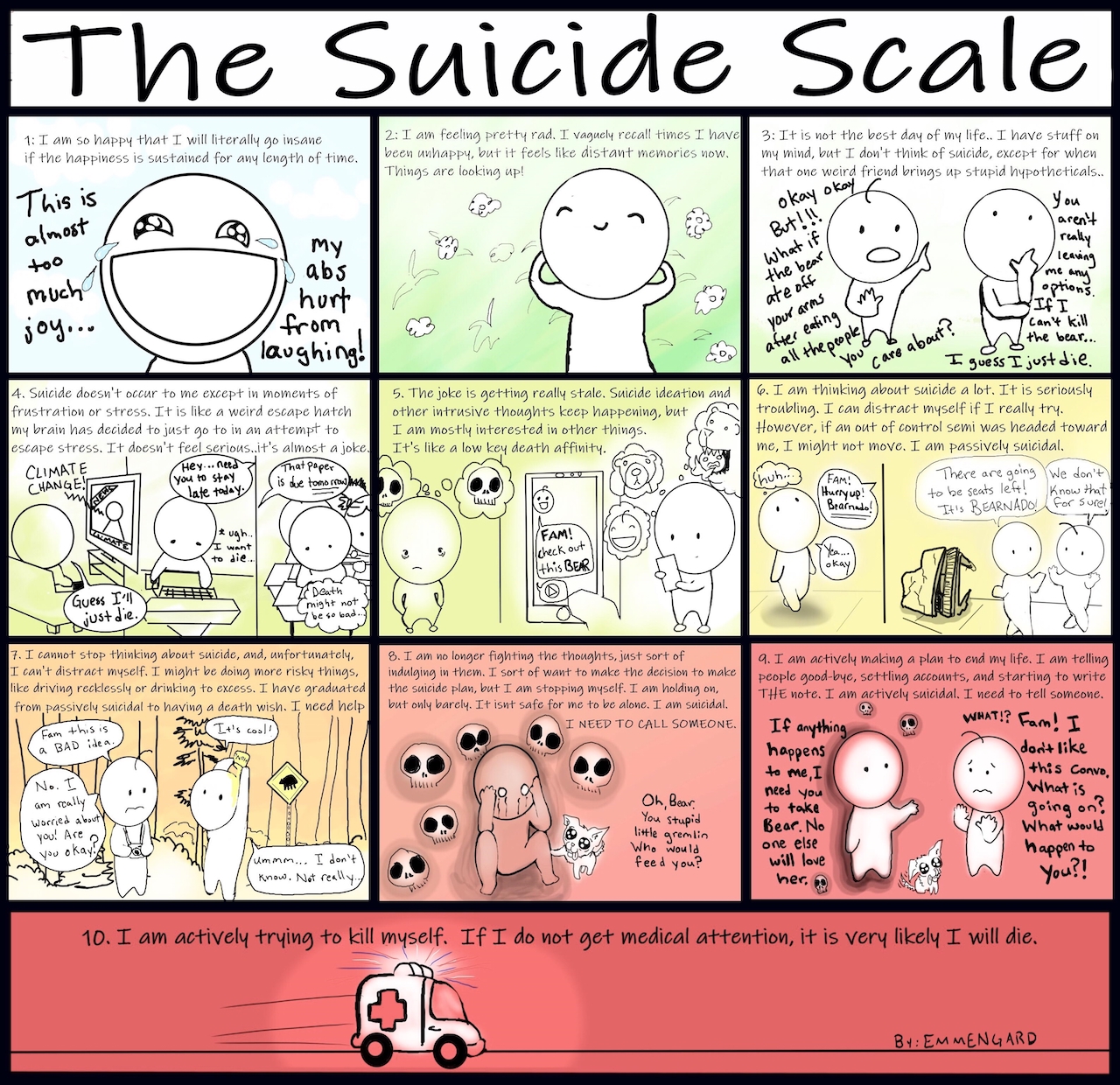
This Suicide Scale Can Help Others Understand Your Suicidal Thoughts
DOD Releases Report on Suicide Among Troops, Military Family Members