Unlock Accessibility: What Is Skip Navigation & How To Use It
Are you lost in the labyrinth of website menus, endlessly scrolling and clicking?The solution is here: Skip navigation, a streamlined approach to web browsing that catapults you directly to the heart of the content.
This seemingly simple feature offers profound benefits, especially for individuals utilizing assistive technologies like screen readers, or anyone who values speed and efficiency in their online experience. Imagine bypassing the repetitive navigation bar with a single click, landing instantly on the information you seek.
Skip navigation links, strategically placed at the top of a webpage, are typically labeled with clear instructions such as "Skip to main content" or "Skip navigation." Upon activation, these links seamlessly transport you to the primary heading of the page, usually the starting point of the core content.
- Guide Is Vegamovies 4k Hd Really Safe Legal Find Out
- Discover Mary Burke Her Story Career And Impact On Wisconsin
Consider skip navigation as an unsung hero of web accessibility, silently enhancing the browsing experience for everyone. It's about more than just convenience; it's about ensuring equitable access to information for all users, regardless of their abilities or browsing habits.
| Skip Navigation: Feature Overview | |
|---|---|
| Purpose | To allow users to bypass the navigation bar and directly access the main content of a webpage. |
| Benefits |
|
| Typical Location | Top of the webpage, often as the first focusable element. |
| Common Labels | "Skip to Main Content", "Skip Navigation", "Jump to Content". |
| Target Users |
|
| WCAG Relevance | Addresses WCAG guidelines related to keyboard accessibility and providing mechanisms to bypass blocks of content. |
| SEO Implications | Can improve crawlability by ensuring search engines quickly access main content. |
| Implementation Notes | Should be visually hidden but focusable via keyboard (using CSS techniques). Should lead directly to the beginning of the main content area. |
| Example Code Snippet | Skip to Main Content |
| Further Reading | Understanding WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.1: Bypass Blocks |
Skip Navigation
Introduction: Highlighting the importance of the key aspects.Key Aspects: List key aspects with brief descriptions.Discussion: Detailed discussion on the key aspects, through examples, connections, or linkage to the main topic.Explore the connection between "{point}" and "skip navigation" for content details list. Never use first and second-person pronouns and AI-style formalities.{point}Introduction
{point}Introduction
Skip Navigation
Skip navigation, in essence, is a digital shortcut, a pathway designed to circumvent the typical navigational elements of a website and transport the user directly to the main content. This is particularly advantageous for those relying on assistive technologies, such as screen readers, or for individuals who simply prefer a more direct and efficient route to the information they seek.
- Accessibility: Skip navigation stands as a cornerstone of web accessibility, empowering users with disabilities to navigate websites with greater ease and independence.
- Efficiency: This feature acts as a time-saver, allowing users to bypass redundant content and swiftly access the information that holds the most relevance to their needs.
- User experience: By streamlining the path to desired content, skip navigation elevates the overall user experience, fostering a sense of control and satisfaction.
- Search engine optimization (SEO): Skip navigation contributes to improved SEO by facilitating search engine indexing of the page's primary content, making it more discoverable.
- Compliance: Adhering to accessibility standards, such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), is made easier through the implementation of skip navigation.
Ultimately, the inclusion of skip navigation represents a commitment to inclusivity and user-centric design, transforming websites into more accessible, efficient, and enjoyable platforms for all. Its a testament to the power of thoughtful design in shaping a better online experience.
- Discover Vgamovies Com Your Free Video Game Library More
- Gianna Michaels 2024 The Rise Of Progressive Politics Explained
Accessibility
Accessibility, in the context of web design, goes beyond mere aesthetics; it's about ensuring that digital spaces are usable and navigable for everyone, regardless of their abilities or disabilities. Skip navigation plays a pivotal role in this endeavor, providing a means for users with disabilities to bypass navigational clutter and access the core content directly. This is particularly vital for those using screen readers or facing challenges with traditional mouse or trackpad navigation.
- Improved navigation for users with visual impairments: For individuals with visual impairments, skip navigation is a lifeline, allowing them to sidestep lengthy navigation menus and jump directly to the content they need. This is especially crucial for screen reader users, who rely on sequential reading of webpage elements.
- Faster access to content for users with mobility impairments: Skip navigation offers a streamlined path to content for users with mobility impairments, reducing the need for precise mouse movements or repetitive keystrokes. This simple feature can significantly improve their browsing speed and overall experience.
- Simplified navigation for users with cognitive disabilities: Complex navigation structures can be overwhelming for users with cognitive disabilities. Skip navigation provides a clear and direct route to the main content, reducing cognitive load and improving comprehension.
- Improved accessibility for all users: While primarily benefiting users with disabilities, skip navigation also enhances the browsing experience for all users. By offering a quick and easy way to bypass navigation, it streamlines access to information and improves overall usability.
The implementation of skip navigation is not just a matter of compliance; it's a reflection of a commitment to creating a more inclusive and accessible digital world. It acknowledges the diverse needs of users and strives to provide an equitable browsing experience for everyone.
Efficiency
In the fast-paced digital landscape, time is a precious commodity. Skip navigation emerges as a champion of efficiency, allowing users to bypass extraneous content and zoom directly to the information they seek. This is particularly valuable for those searching for specific details on a webpage or simply trying to accomplish tasks quickly.
Imagine a user searching for a company's contact information. Instead of painstakingly navigating through multiple menus and scrolling through irrelevant content, they can utilize skip navigation to jump directly to the contact section, saving valuable time and effort.
The benefits extend to users of assistive technologies, such as screen readers. These tools, while essential for accessibility, can sometimes be slow and cumbersome when navigating complex menus. Skip navigation allows users to bypass these menus and access the main content directly, significantly improving their browsing speed and efficiency.
Efficiency, in the context of web design, translates to user satisfaction. By providing a streamlined and direct path to information, skip navigation empowers users to accomplish their goals quickly and effectively, fostering a positive and productive online experience.
User experience
User experience (UX) encompasses the holistic perception and interaction a user has with a website or application. Skip navigation, often overlooked, plays a vital role in shaping a positive UX by simplifying navigation and providing a direct route to desired content.
Consider the user who is pressed for time or seeking a specific piece of information. Skip navigation offers a convenient shortcut, allowing them to bypass the navigation bar and jump directly to the relevant section of the page. This eliminates frustration and empowers users to find what they need quickly and easily.
For users relying on assistive technologies like screen readers, skip navigation is even more crucial. By bypassing complex navigation menus, it streamlines the browsing experience and reduces the cognitive load, allowing users to focus on the content itself.
A well-designed website should prioritize user needs and strive to provide a seamless and intuitive experience. Skip navigation embodies this principle by offering a simple yet effective way to improve navigation and enhance overall user satisfaction.
Search engine optimization (SEO)
While primarily focused on accessibility and user experience, skip navigation also indirectly contributes to search engine optimization (SEO). By ensuring that search engines can easily access and index the main content of a page, it helps to improve a website's visibility in search results.
- Improved indexing: Skip navigation facilitates the indexing of a website's main content by providing a clear path for search engine crawlers. This ensures that the most important information on the page is properly recognized and categorized.
- Increased organic traffic: By improving indexing, skip navigation can lead to increased organic traffic. When search engines accurately understand the content of a page, they are more likely to display it in relevant search results, attracting more users to the website.
- Improved user experience: A positive user experience is a key factor in SEO. Skip navigation contributes to a better UX by making it easier for users to find what they need, which can lead to increased engagement and lower bounce rates, further boosting search engine rankings.
SEO is not just about keywords and backlinks; it's about creating a website that is both user-friendly and search engine-friendly. Skip navigation embodies this holistic approach by improving both accessibility and discoverability.
Compliance
Compliance with accessibility regulations, such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), is not just a legal requirement; it's a moral imperative. Skip navigation plays a crucial role in achieving WCAG compliance by ensuring that websites are accessible to people with disabilities.
WCAG 2.1 outlines specific requirements for skip navigation, including:
- Skip navigation links must be present on all pages.
- These links must be easily discoverable and usable.
- They must lead directly to the main content of the page.
By implementing skip navigation, website owners demonstrate a commitment to inclusivity and ensure that their websites are accessible to a wider audience, regardless of their abilities.
Examples of how skip navigation enhances accessibility:
- For users with visual impairments, it provides a direct route to the main content, bypassing irrelevant navigation elements.
- For users with motor impairments, it eliminates the need for precise mouse movements, simplifying navigation.
- For users with cognitive disabilities, it reduces cognitive load by providing a clear and direct path to the information they seek.
Compliance with accessibility regulations is not just about ticking boxes; it's about creating a more equitable and inclusive digital world. Skip navigation is a key element in this effort, ensuring that websites are accessible to everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions about Skip Navigation
Skip navigation, as we've discussed, is a powerful tool for enhancing web accessibility and user experience. However, some common questions often arise regarding its implementation and purpose.
Question 1: Is skip navigation exclusively for users with disabilities?
Answer: While skip navigation provides significant benefits for users with disabilities, it's not exclusively for them. Anyone can utilize it to quickly access the main content of a webpage, regardless of their abilities.
Question 2: Is skip navigation legally mandated?
Answer: While not universally mandated by law, skip navigation is considered a best practice for website development. Implementing it demonstrates a commitment to accessibility and can help organizations comply with regulations like the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) in some contexts.
Summary of key takeaways or final thought: Skip navigation is a versatile feature that enhances accessibility, usability, and SEO. Its implementation is a testament to a commitment to inclusivity and user-centric design.
- Breaking Gabe Watson And Kim Lewis Are They Still Together Find Out
- Exploring The Enigmatic Aylla Gattina Unveiling The Wild Cat
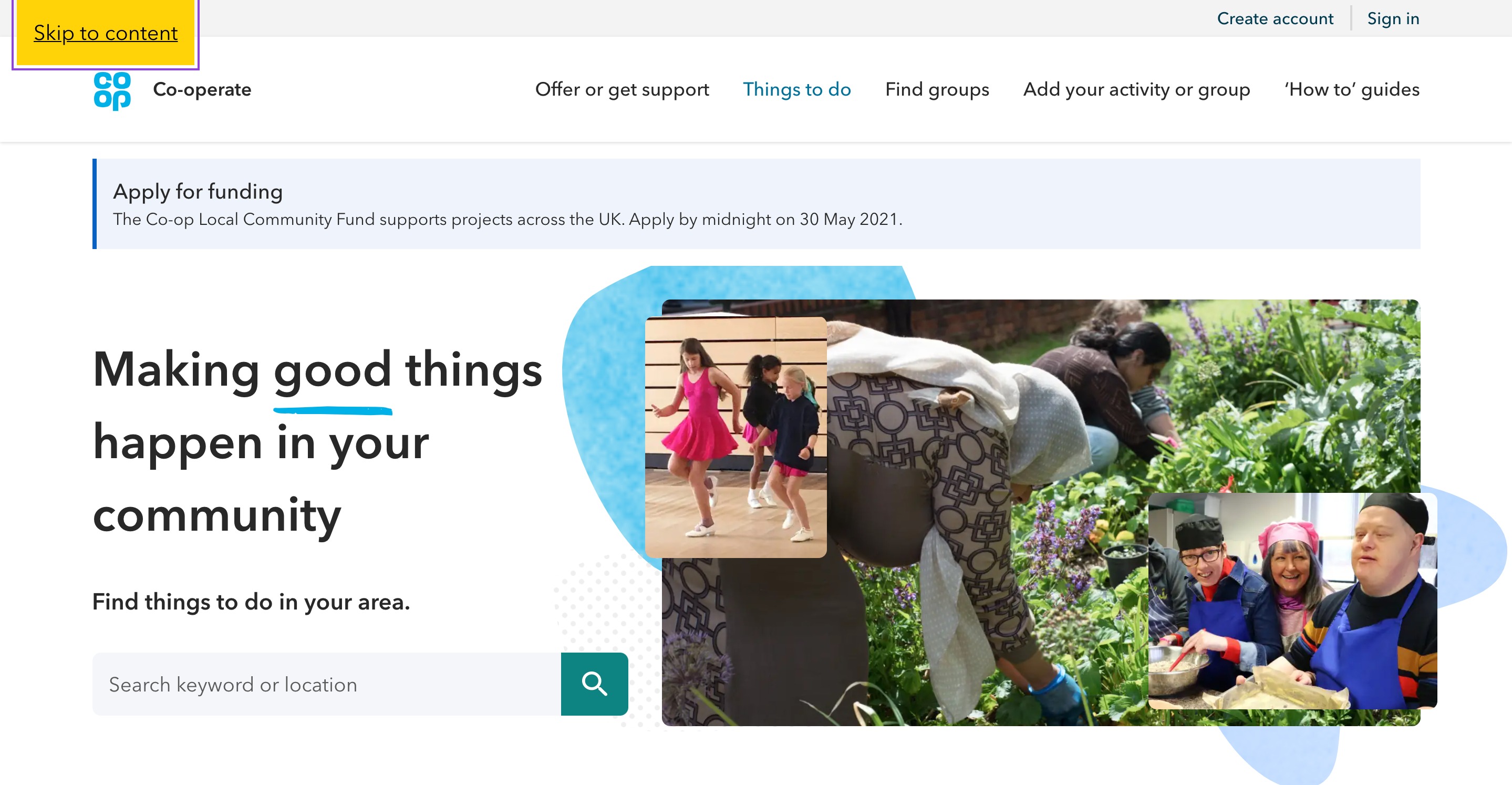
Skip navigation Coop Experience Library

What Is Skip Navigation Link and Why Is It Useful? Pine

Why You Should Add "Skip Navigation" Links to Your Website AEL Data